
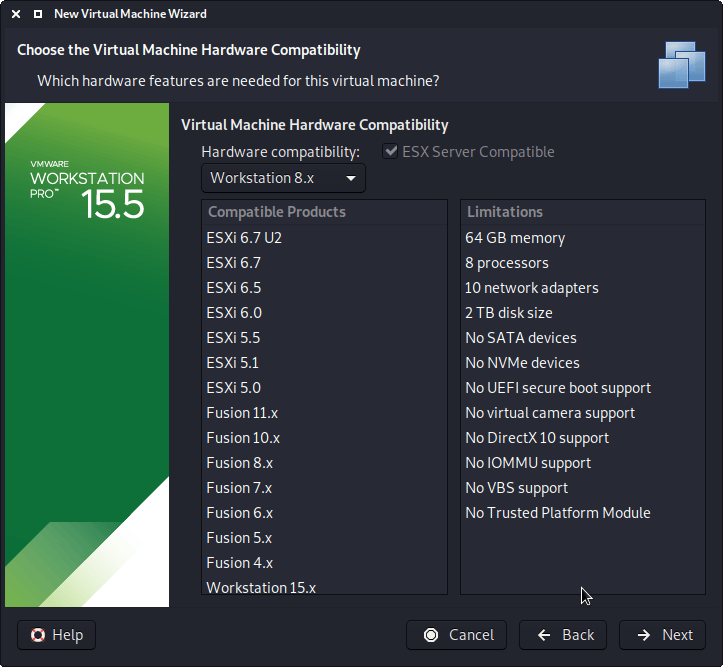
- Kali vmware vs virtualbox install#
- Kali vmware vs virtualbox update#
- Kali vmware vs virtualbox software#
- Kali vmware vs virtualbox license#
- Kali vmware vs virtualbox iso#
Kali vmware vs virtualbox software#
The software allows you to run virtual machines on your host operating system.
Kali vmware vs virtualbox license#
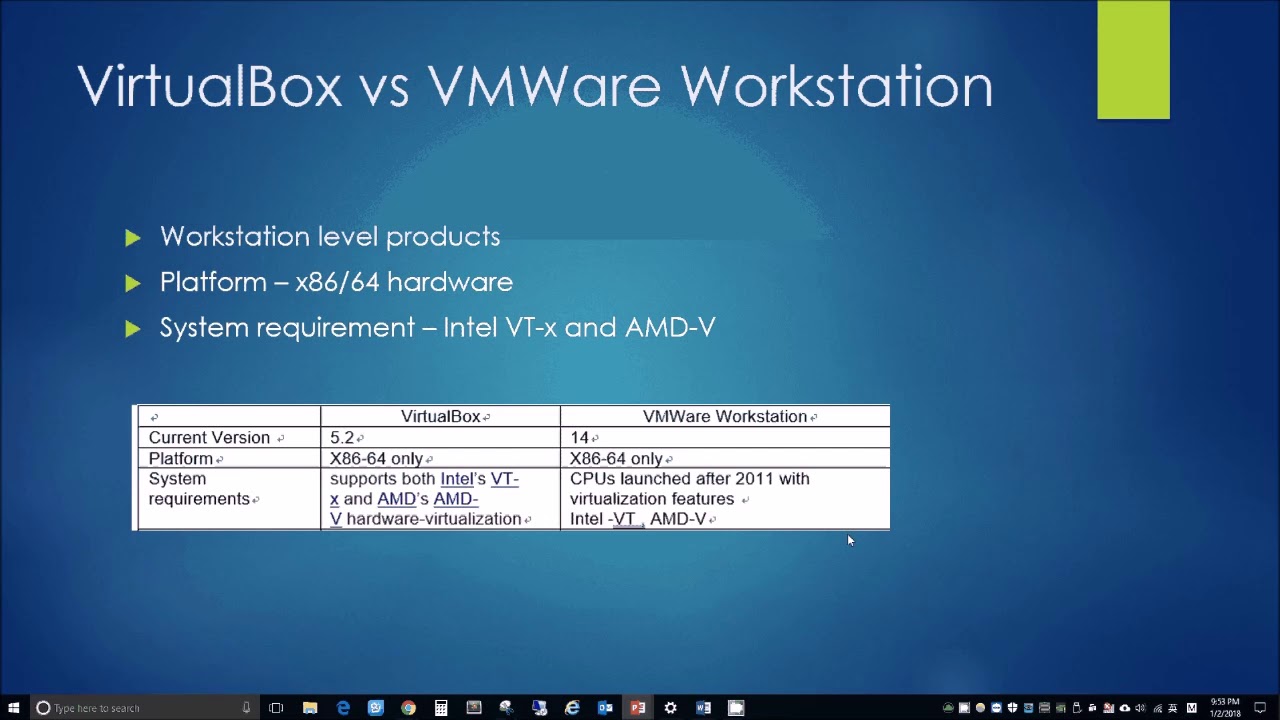
It is a free, open-source virtualization product, distributed under the GNU General Public License (GPL) version 2. VirtualBox is Oracle’s x86 and AMD64/Intel64 virtualization software. In this tutorial, you will learn about the difference between VirtualBox and VMware. While type 1 is more suitable for large production environments, hosted hypervisors are used for VMs run on personal computers. The most popular type 2 hypervisor software are VirtualBox and VMware. Type 2 (hosted) hypervisors, installed on top of the host operating system.Type 1 bare metal hypervisor, which are installed on the physical server.They don’t see the host OS nor other VMs running on the same resources. The hypervisor emulates resources so the guest operating systems assume they are using all physical resources. The virtualization layer that abstracts the guest machine and underlying operating system is created with a hypervisor. Doing so reduces the number of physical dedicated servers required. Server virtualization allows you to run multiple operating systems on the same physical resources. It is used by everyone, from enthusiasts to developers. If you want to manually re-install it, you can see our VirtualBox Guest Guide.Virtualization has become the norm for software and OS testing.
Kali vmware vs virtualbox install#
If it is, should then automatically install any additional tools (such as virtualbox-guest-x11) to give a better user experience.
Kali vmware vs virtualbox iso#
We will now press “Add”, then navigate to where our ISO is located.Īfter pressing “Open”, we can see its been added, so we make sure its selected and press “Choose”.Īll that is left now to do is press “Start”.Īfter all this is done, we save, start up the VM, and then continue installing Kali Linux as we normally would for a bare metal install.ĭuring Kali Linux setup process, the install wizard should detect if its inside a VM. We want to use our Kali image, rather than a physical drive, so we select the icon to the side of the drop down.Ī new pop up will open, “Optical Disk Selector”. The first time we run it, we will get a prompt saying do we wish to mount an image to use as a “start-up disk”. The final settings view looks like the following: In “Display” -> “Screen”, we make sure to have “Video Memory” set to 128 MBĪnother item to point out is to make sure that “Accelerated 3D graphics” is disabled, as people have reported that causes issues. In “System” -> “Processor”, we increase the “Processor(s)” to be 2.Īt the same time, we also enable “Extended Features” for Enable PAE/NX. In “System” -> “Motherboard”, we change the “Boot Order” to make sure Hard Disk is top and Optical is the second. In “General” -> “Advanced”, we make sure to set “Shared Clipboard” to bidirectional, as well as “Drag’n’Drop” to bidirectional Now we click on “Settings”, to customize the VM further. We use 80.00 GB for our VMs.Īfter clicking on “Create”, the wizard is complete. Now with “File location and size”, we can now define how large the virtual hard disk will be. This screen below, “Hard disk”, allows us to Create a new virtual disk now.įor the “Hard disk file type”, we select VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image) (and its the default option).įor the following screen, “Storage on physical hard disk”, we go with the default option of Dynamically allocated. When we make the general VMs, we select 2048 MB (2GB) for RAM, but we often increase this for our personal machines as we have high-performing devices with spare RAM which Kali can utilize. Various tools inside of Kali can be demanding of resources. Again, the higher the amount of RAM, the more applications can be open and at increased performance. “Memory size” is the next section, where we can define how much RAM to use.

For the “Version”, we are going to be using the 圆4 desktop image, so we are going to select Debian (64-bit). Example: kali-linux-2021.3-vbox-amd64).įor the “Type”, we set it as Linux.
Kali vmware vs virtualbox update#
We are keeping it generic in this guide (as Kali is a rolling distribution, and we update it), however for our releases, we use the version number in the name as it is a fixed release ( kali-linux-YYYY.N-vbox-ARCH. This name is also used in any filenames (such as the configuration, hard disk and snapshot - which isn’t changed from this point). The next screen is “Name and operating system” which is where you name the VM. Upon starting up VirtualBox, select “New” (Machine -> New). You may need to enable virtualization in your BIOS/UEFI for (e.g.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
